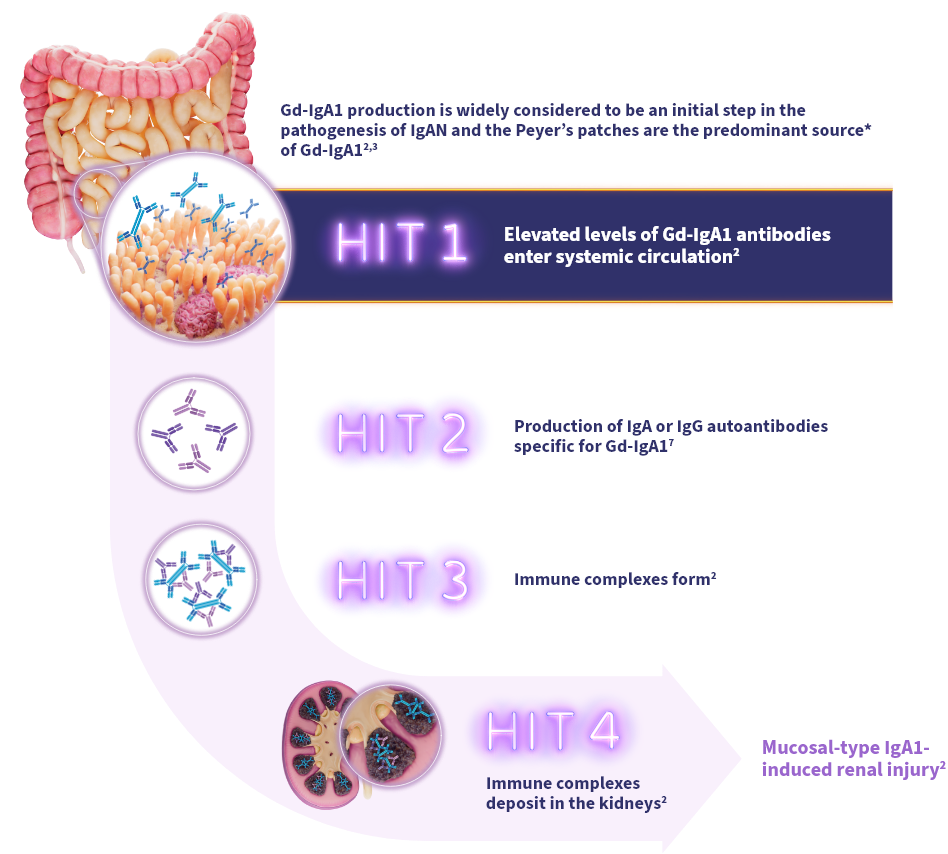
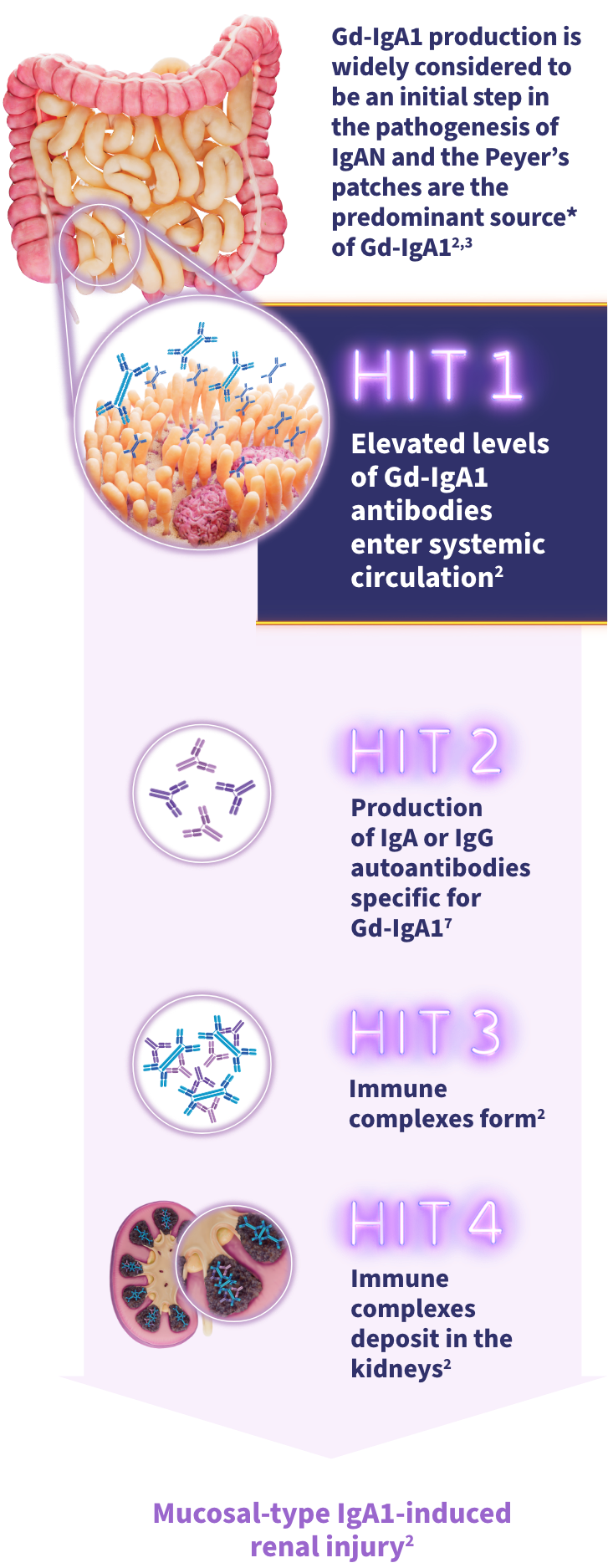
Elevated systemic Gd-IgA1 can lead to immune complex formation and mesangial deposition1The gut-kidney axis plays a significant role in the pathophysiology of IgAN2
- Gd-IgA1 is an emerging biomarker and is widely considered to be an initial step in IgAN pathogenesis3,4
- Peyer's patches are thought to be a predominant source of Gd-IgA1 in IgAN2
NEARLY

of Peyer’s patch tissue has been shown to be found in the distal ileum5,6
IgAN is a progressive immune-mediated disease where early modulation is important2,3
The widely accepted 4-HIT model illustrates the pathogenesis of IgAN3:
In the phase 3 NefIgArd trial, levels of circulating Gd-IgA were reduced from baseline at 3, 6, and 9 months with TARPEYO + RASi vs RASi alone. Data are exploratory. Clinical significance has not been established. Small sample sizes of a specific patient group are limitations of these analyses.
*Mucosal B cells present in the ileum, including the Peyer’s patches, express glucocorticoid receptors, and are responsible for the production of Gd-IgA1 causing IgAN. Through their anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects at the glucocorticoid receptor, corticosteroids can modulate B cell numbers and activity. It has not been established to what extent the efficacy of TARPEYO is mediated via local effects in the ileum vs systemic effects.7,9 †TARPEYO was studied under the name Nefecon, which was used in the 2025 KDIGO guideline.

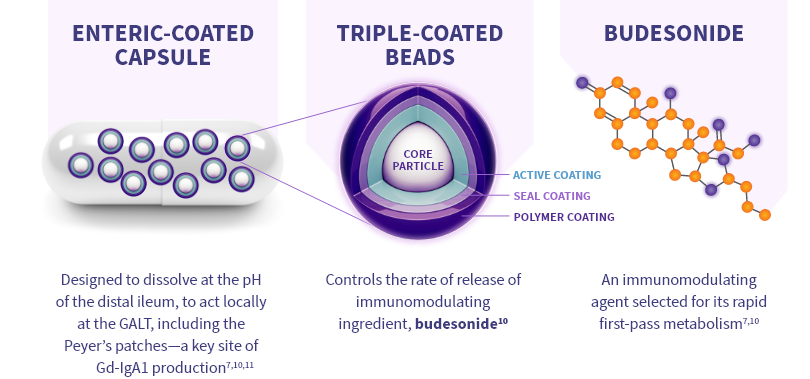
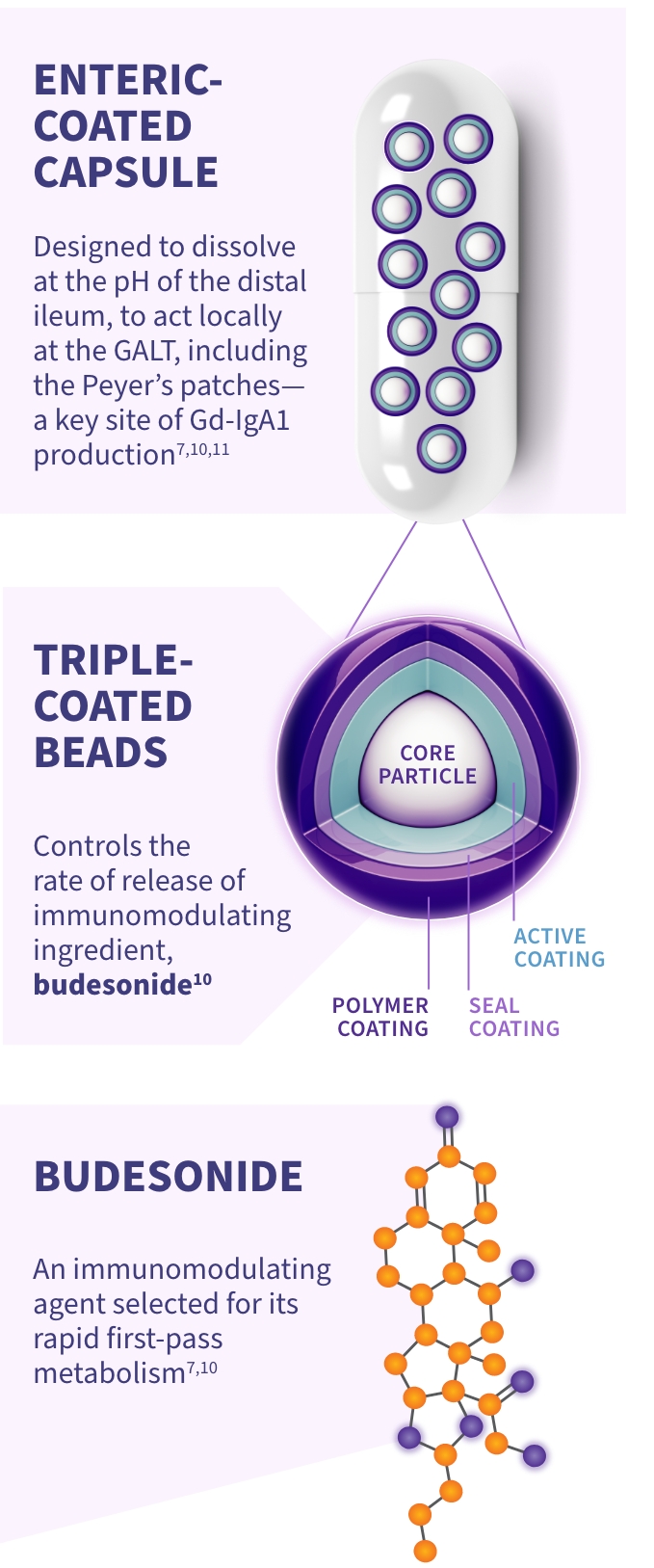
TARPEYO is designed to locally target a key site of Gd-IgA1 production10*
Budesonide is a locally acting glucocorticoid designed to limit the systemic exposure due to a high rate of first-pass liver metabolism10
It has not been established to what extent the efficacy of TARPEYO is mediated via local effects in the ileum vs systemic effects.
*Mucosal B cells present in the ileum, including the Peyer’s patches, express glucocorticoid receptors, and are responsible for the production of Gd-IgA1 causing IgAN. Through their anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects at the glucocorticoid receptor, corticosteroids can modulate B cell numbers and activity.7,9
TARPEYO is designed to target the distal ileum, including the Peyer’s patches, to treat IgAN at a key site* of Gd-IgA1 production7,11
Local action and first-pass metabolism
- Budesonide is a locally acting glucocorticoid designed to limit systemic exposure due to high rate of first-pass liver metabolism10
Shorter half-life and exposure duration
- In pharmacokinetic studies comparing TARPEYO and Entocort® EC (budesonide), TARPEYO exhibited higher maximum plasma concentrations of budesonide while having a shorter terminal half-life, indicating a shorter duration of systemic exposure to budesonide13
Clinical significance is unknown.
Prolonged retention
- Developed for topical use on mucosal surfaces, budesonide exhibits rapid absorption and prolonged retention in mucosal tissue10
It has not been established to what extent the efficacy of TARPEYO is mediated via local effects in the ileum vs systemic effects.
In the phase 3 NefIgArd trial, levels of circulating Gd-IgA1 were reduced from baseline at 3, 6, and 9 months with TARPEYO + RASi vs RASi alone. Data are exploratory. Clinical significance has not been established. Small sample sizes of a specific patient group are limitations of these analyses.
*Mucosal B cells present in the ileum, including the Peyer’s patches, express glucocorticoid receptors, and are responsible for the production of Gd-IgA1 causing IgAN. Through their anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects at the glucocorticoid receptor, corticosteroids can modulate B cell numbers and activity.7,9
TARPEYO is the only formulation of budesonide designed to target the Peyer’s patches of the ileum10,14
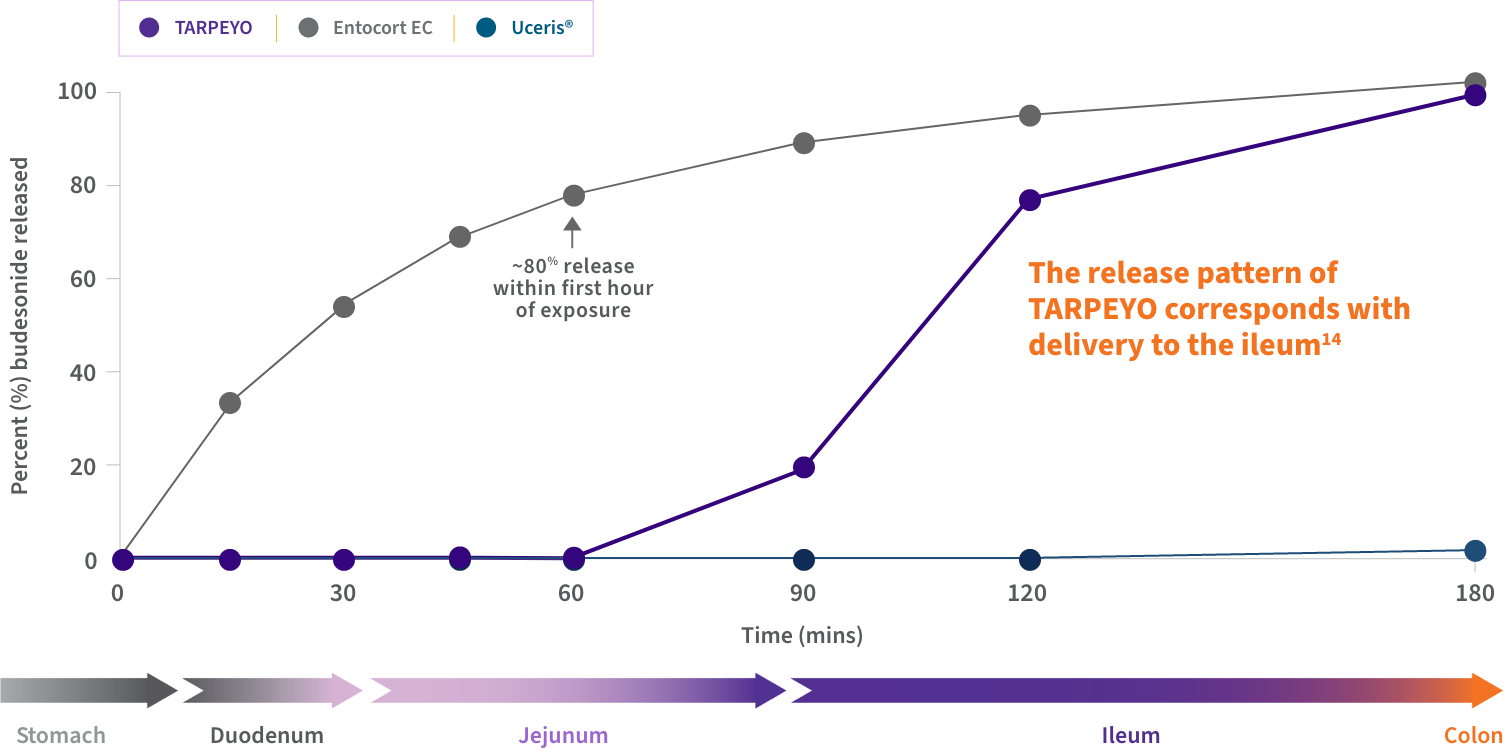
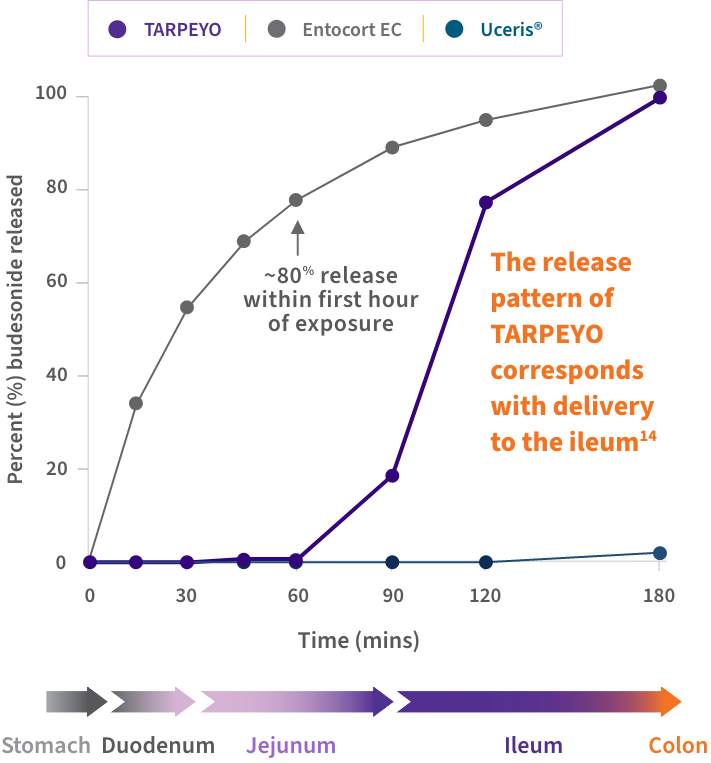
An in vitro study compared the release patterns of commercially available oral budesonide products. Its aim was to determine if the products are interchangeable regarding their delivery of budesonide to the GI tract.14*
Findings suggest that the release pattern of TARPEYO is consistent with the intended design of the product, to deliver budesonide to the Peyer’s patch-rich area of the ileum.15
Dissolution profiles of 3 delayed-release budesonide oral formulations14,15
Approximate GI tract transit time (highly variable; illustrative only and not intended to compare efficacy and safety). TARPEYO was studied under the name Nefecon.
- TARPEYO demonstrated a unique dissolution profile compared to other budesonide formulations, including Entocort EC14
- The release pattern of TARPEYO indicates that the delivery of budesonide would occur in the ileum14
*Dissolution test conditions were conducted based on EMA, FDA, and USP guidelines.14
POST HOC SUBANALYSIS: Reductions in Gd-IgA1 were seen with TARPEYO10,16*†
In a post hoc biomarker subanalysis of NefIgArd, serum Gd-IgA1 was reduced at months 3, 6, and 910,16
Percent (%) change in Gd-IgA1 with TARPEYO + RASi vs RASi alone10

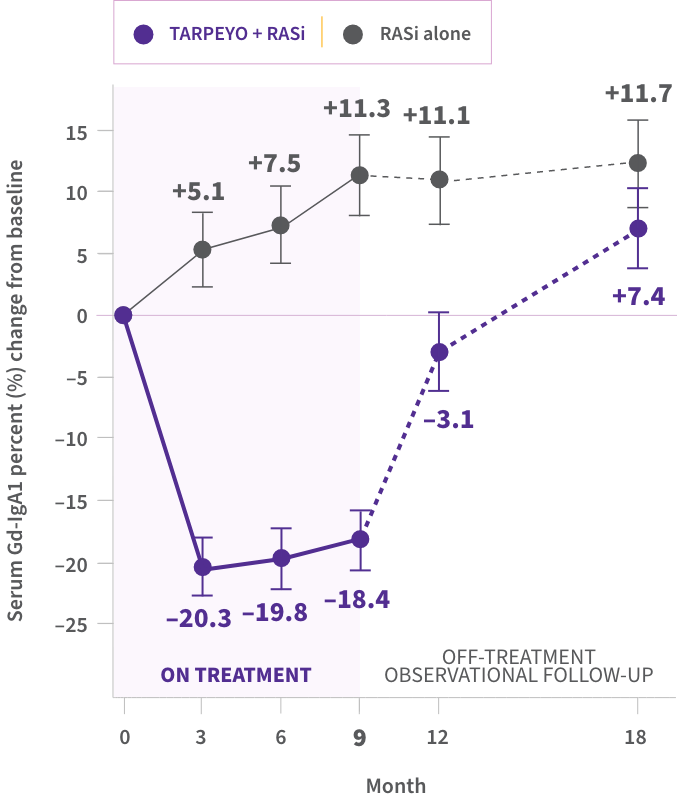
Data are exploratory. Clinical significance has not been established. Small sample sizes of a specific patient group are limitations of these analyses. Additional longitudinal studies of more diverse patient cohorts are needed to validate findings.
- Reductions in IgG anti-IgA autoantibodies and IgA-containing immune complexes were also seen with TARPEYO16
*Data from Part A of the Phase 3 NeflgArd trial. †Mucosal B cells present in the ileum, including the Peyer’s patches, express glucocorticoid receptors, and are responsible for the production of Gd-IgA1 causing IgAN. Through their anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects at the glucocorticoid receptor, corticosteroids can modulate B cell numbers and activity. It has not been established to what extent the efficacy of TARPEYO is mediated via local effects in the ileum vs systemic effects.7,9 ‡TARPEYO was studied under the name Nefecon, which was used in the KDIGO 2025 guideline.
EMA=European Medicines Agency; FDA=Food and Drug Administration; GALT=gut-associated lymphoid tissue; Gd-IgA1=galactose-deficient IgA1; GI=gastrointestinal; IgA=immunoglobulin A; IgG=immunoglobulin G; KDIGO=Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes; RASi=renin-angiotensin system inhibitor; USP=United States Pharmacopeia.
REFERENCES: 1. Lim RS, Yeo SC, Barratt J, et al. An update on current therapeutic options in IgA nephropathy. J Clin Med. 2024;13(4):947. doi:10.3390/jcm13040947 2. Barratt J, Rovin BH, Cattran D, et al. Why target the gut to treat IgA nephropathy? Kidney Int Rep. 2020;5(10):1620-1624. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2020.08.009 3. Chang S, Li X-K. The role of immune modulation in pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:92. doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00092 4. Kim JS, Hwang HS, Sang HL, et al. Clinical relevance of serum galactose deficient IgA1 in patients with IgA nephropathy. J Clin Med. 2020;9:3549. 5. Jung C, Hugot J-P, Barreau F. Peyerʼs patches: the immune sensors of the intestine. Int Journal Inflammation. 2010;1-12. https://doi.org/10.4061/2010/823710 6. Van Kruiningen H, West AB, Freda BJ, et al. Distribution of Peyerʼs patches in the distal ileum. Inflammatory Bowel Dis. 2002;8(3):180-185. https://doi.org/10.1097/00054725-200205000-00004 7. TARPEYO. Prescribing Information. Calliditas Therapeutics AB; June 2024. 8. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). KDIGO 2025 clinical practice guideline for the management of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) and immunoglobulin A vasculitis (IgAV). Kidney Int. 2025;108:S1-S71. 9. Lafayette R, Kristensen J, Stone A, et al. Efficacy and safety of a targeted-release formulation of budesonide in patients with primary IgA nephropathy (NefIgArd): 2-year results from a randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2023. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01554-4 10. Data on file. Calliditas Therapeutics AB. 11. Barratt J, Kristensen J, Stone A, et al. Nefecon treatment provides kidney benefits for patients with IgAN that extend to those with low levels of UPCR: a sub-analysis of the phase III NefIgArd trial. Kid Int Rep. 2024;9:S1-S662. 12. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, et al. FDA Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations. 45th Edition. 2025. Accessed October 30, 2025. https://www.fda.gov/media/71474/download?attachment 13. Barratt J, Kristensen J, Pedersen C, Jerling M. Insights on Nefecon®, a targeted-release formulation of budesonide and its selective immunomodulatory effects in patients with IgA nephropathy. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024;18:3415-3428. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S383138 14. Dressman, J. Comparative dissolution of budesonide from four commercially available products for oral administration: implications for interchangeablity. Dissolution Technol. 2023;30(4):224-229. 15. Dressman J, Philipson R, Barratt J. Comparison of the dissolution profile of Nefecon with three other commercially available oral formulations of budesonide: Implications for interchangeability. Poster presented at: IIgANN Congress; September 28-30, 2023; Tokyo, Japan. 16. Khan I, Nawaz N, Jama AAA, et al. Effects of nefecon on Hits 1, 2, and 3 of the IgAN pathogenic cascade: a full NefIgArd analysis. Leicester IgAN research group: Poster presented at 62nd ERA Congress. June 4-7, 2025; Vienna, Austria.