NefIgArd: the first Phase 3 IgAN trial to assess off-treatment effect with a 15-month observational period1,2
Primary endpoint at full study completion: time-weighted average of eGFR over 2 years (N=364)1*
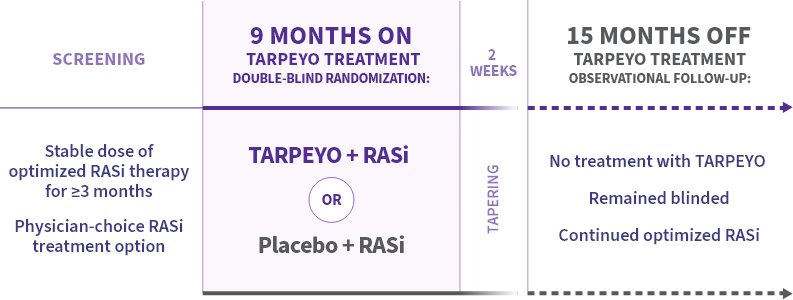
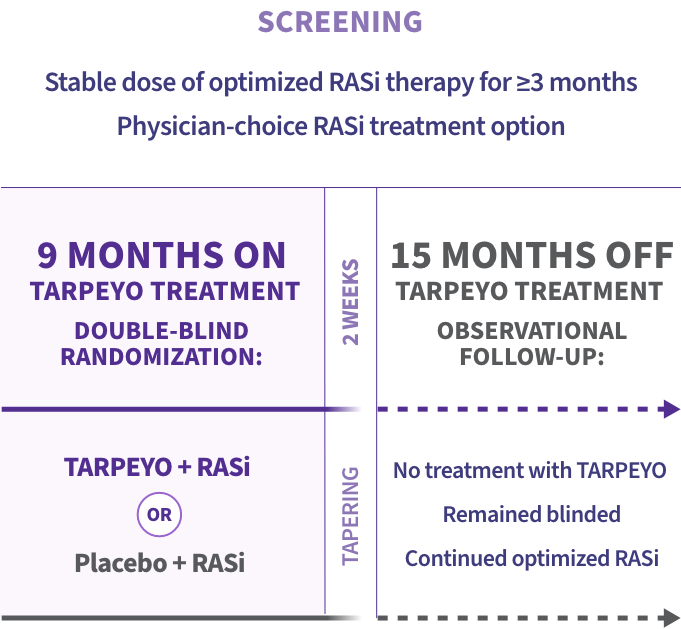
*The primary endpoint for the interim analysis was UPCR at 9 months compared to baseline (N=199).1
Key inclusion criteria2
Adult patients with:
- Biopsy-confirmed IgAN diagnosis
- Persistent proteinuria ≥1 g/day or UPCR ≥0.8 g/g in 2 consecutive measurements
- eGFR 35 to 90 mL/min/1.73 m2
- Receiving RASi therapy (ACEis and/or ARBs) at the maximum allowed/tolerated dose 3 months prior to randomization
Blood pressure and diabetes were well controlled and no prophylaxis with antibiotics was required.1,2
Select baseline characteristics2
| TARPEYO + RASi | RASi alone | |
|---|---|---|
Median age (range) |
43 (36 to 50) | 42 (34 to 49) |
Median baseline UPCR (interquartile range) |
1.28 (0.90 to 1.76) | 1.25 (0.88 to 1.74) |
Median baseline eGFR (interquartile range) |
56.14 mL/min/ 1.73 m2 (45.50 to 70.97) |
55.11 mL/min/ 1.73 m2 (45.96 to 67.74) |
<60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 |
109 (60%) |
109 (60%) |
≥60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 |
73 (40%) |
73 (40%) |
Median time from IgAN diagnosis (interquartile range) |
2.4 years (0.6 to 6.9) | 2.6 years (0.6 to 6.5) |
- Blood pressure was well controlled at study entry (recommended target of <125/75 mmHg)1,2
- Majority of patients had not been on prior steroid therapy2
- On average, patients were in Stage 3 CKD at baseline2,3
The only FDA-approved treatment shown to stabilize eGFR while on therapy in a Phase 3 IgAN trial1,4,5
LS mean change in eGFR from baseline to 2 years1*
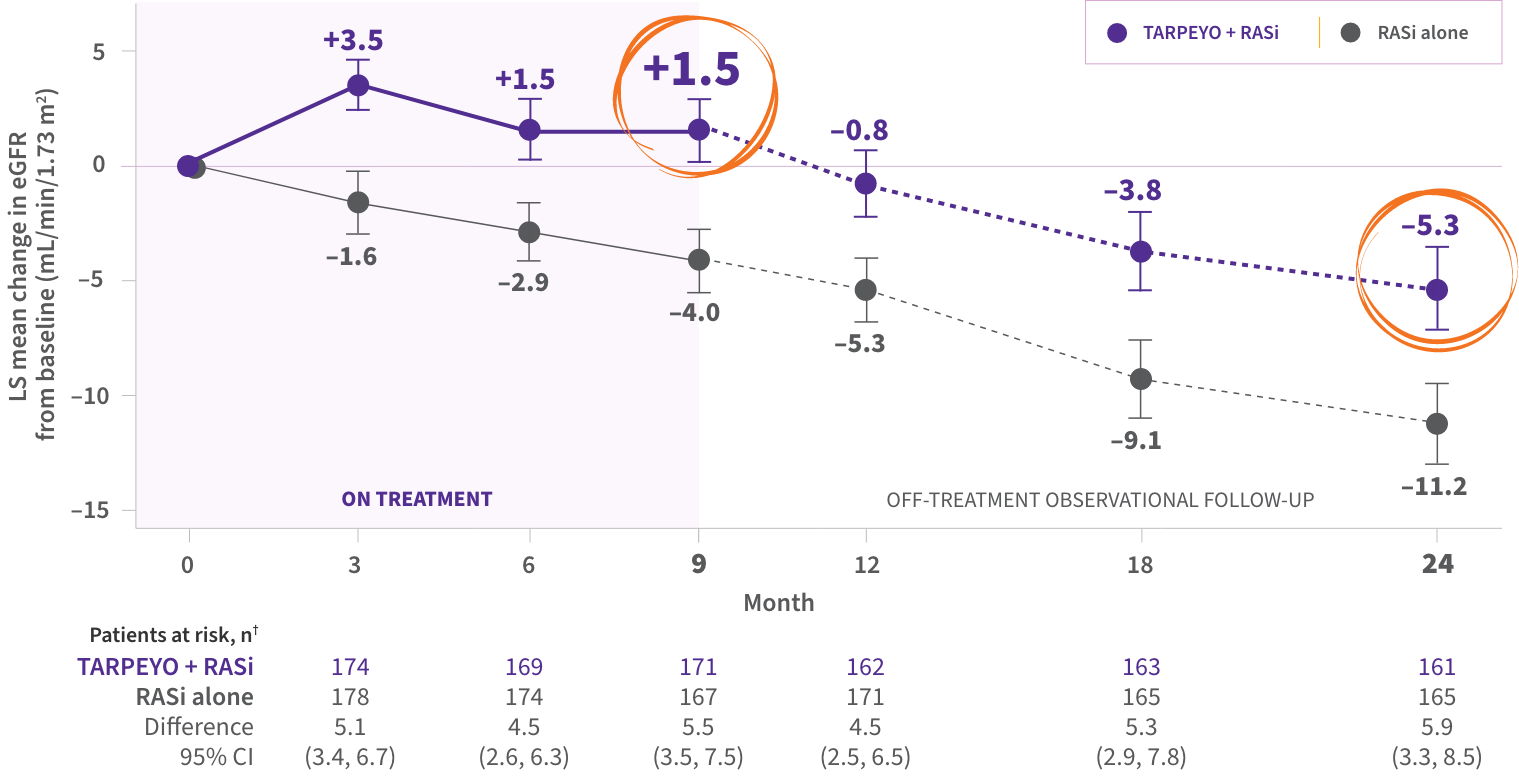
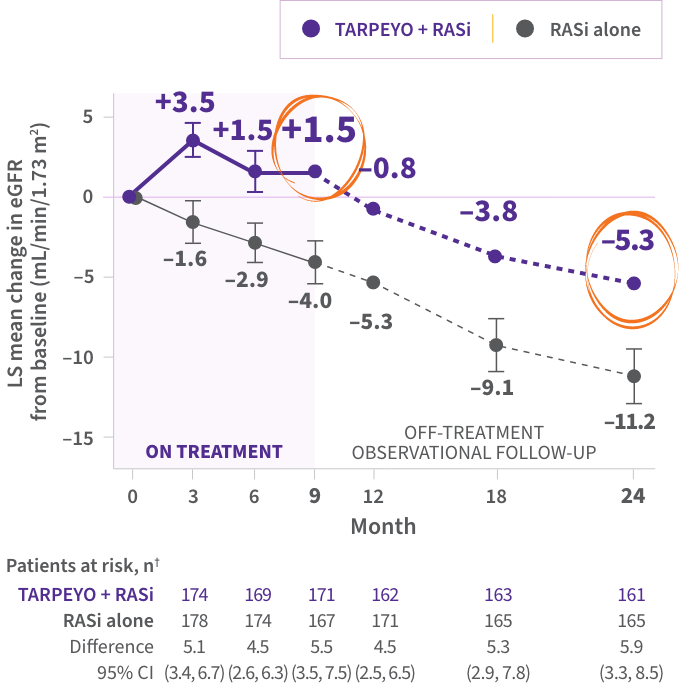
PRIMARY ENDPOINT
- Statistically significant difference of 5.05 mL/min/1.73 m2 over 2 years in favor of TARPEYO + RASi vs RASi alone4‡
kidney function preservation at 2 years with TARPEYO + RASi relative to RASi alone1,4§
The favorable effect of TARPEYO on eGFR was seen as early as month 3 and remained consistent over 2 years.1
The effect of TARPEYO on the long-term rate of decline in kidney function has not been established.1
*Estimated from a mixed-model, repeated-measures analysis using untransformed data up to 24 months, regardless of use of rescue medications.1 †Not all patients in the full analysis set (FAS) contributed data at each time point.1 ‡The primary endpoint for the interim analysis was UPCR at 9 months compared to baseline (N=199).1 §Calculated as relative reduction (9.4% TARPEYO + RASi vs 20.3% RASi alone).1,4

Significant UPCR reduction at 9 months, with 52% reduction achieved at 12 months1
UPCR continued to decrease off treatment from month 9 to month 12 and was durable through 2 years
LS mean percent (%) change in UPCR (g/g) from baseline*†
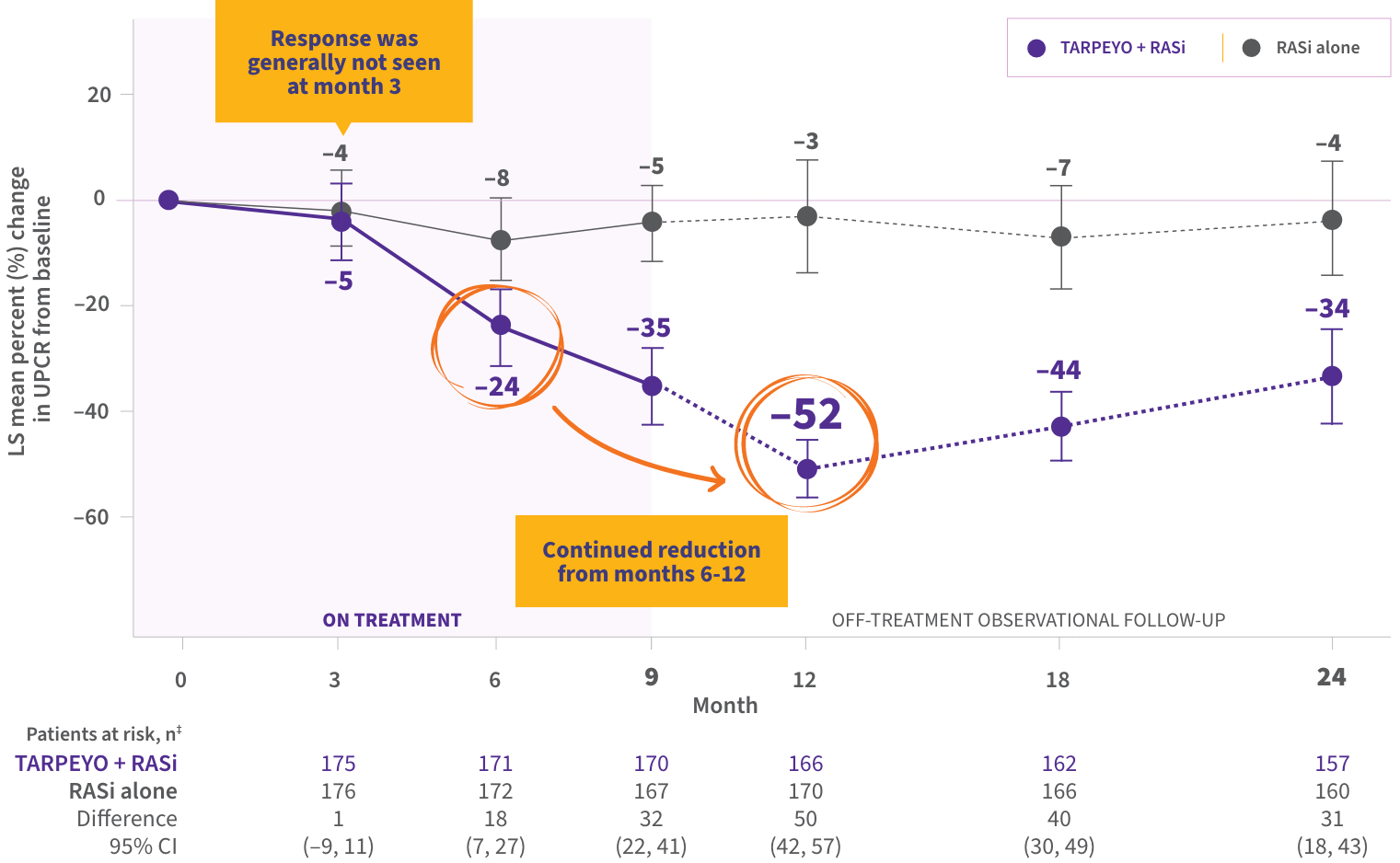

- The mean reduction in UPCR from baseline was 35% at the end of treatment (month 9), with continued reductions off treatment, and a 34% reduction at month 24 (15 months off treatment), demonstrating durability of treatment effect
*Estimated mean percentage change from baseline in UPCR with 95% CI estimated from a mixed-model, repeated-measures analysis of log-transformed post-baseline to baseline ratios, regardless of use of prohibited medications. †Interim analysis at 9 months with the first 199 patients showed a 31% reduction in UPCR in patients treated with TARPEYO + RASi vs RASi alone (95% CI: 16% to 42% reduction; p=0.0001). ‡Not all patients in the FAS contributed data at each time point.
CI=confidence interval; CKD=chronic kidney disease; eGFR=estimated glomerular filtration rate; FAS=full analysis set; Gd-IgA1=galactose-deficient IgA1; KDIGO=Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes; LS=least squares; RASi=renin-angiotensin system inhibitor; UPCR=urine protein-to-creatinine ratio.
REFERENCES: 1. TARPEYO. Prescribing Information. Calliditas Therapeutics AB; June 2024. 2. Lafayette R, Kristensen J, Stone A, et al. Efficacy and safety of a targeted release formulation of budesonide in patients with primary IgA nephropathy (NefIgArd): 2-year results from a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01554-4 3. National Kidney Foundation. Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Accessed October 30, 2025. https://www.kidney.org/kidney-topics/stages-chronic-kidney-disease-ckd 4. Data on file. Calliditas Therapeutics AB. 5. Barratt J, Lafayette RA, Rovin BH, Fellström B. Budesonide delayed release capsules to reduce proteinuria in adults with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023;19(7):699-710. doi:10.1080/1744666X.2023.2206119